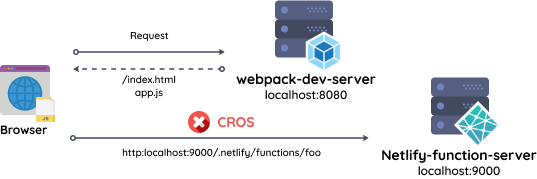
webpack-dev-serverは、webpackを用いた開発用サーバーを立てるためのモジュールです。 Netlify Functionsは、Netlifyの提供するアドオンのひとつで、 AWS Lambdaを実行基盤にしたFaaS(Function as a Service)です。
webpack-dev-serverで立てた開発サーバーからNetlify Functionsで立てたサーバーを呼び出すと、portが違うためCORSの同一オリジンポリシーの制約に引っかかります。
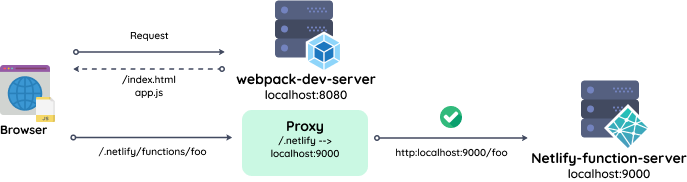
これを回避するには、webpack-dev-serverのプロキシ機能を使います。
動作を確認した環境
- webpack-dev-server v3.9.0
- netlify-lambda v1.6.3
webpackの設定
:webpack.config.jsに次の設定を追記します。
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
// ... 省略 ...
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/.netlify': {
target: 'http://localhost:9000',
pathRewrite: { '^/.netlify/functions': '' }
}
}
}
}:
- webpack-dev-serverに「/.netlify」へのリクエストが来たとき、Netlify Functionのサーバー(
localhost:9000)へフォワードします。 pathRewriteの設定で、「/.netlify/functions」を取り除いた形でのリクエストをバックエンドに投げます。
おまけ:Nuxt.jsの場合
Nuxt.jsを使って作ったページで、axiosを使ってNetlify functionsへリクエストを送ることを考えます。 Nuxt.jsはv2.8.1で確認しました。
Nuxt.jsの設定ファイルnuxt.config.jsは次のように設定します。
module.exports = {
modules: [
'@nuxtjs/axios',
'@nuxtjs/proxy'
],
generate: {
dir: 'dist/client'
},
axios: { baseURL: '/.netlify/functions' },
proxy: {
'/.netlify': {
target: 'http://localhost:9000',
pathRewrite: { '^/.netlify/functions': '' }
}
}
}
Nuxt.jsでのページとNetlify Functionsはこんな感じに作ります。
-
リクエストを送るページ
<template> <main> <input v-model="name" placeholder="Name"></input> <input v-model="message" maxlength="200" type="textarea"></input> <button @click="sendMessage">Send</button> </main> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { name: '', message: '' } }, methods: { async sendMessage() { const params = { name: this.name, message: this.message }; try { const resp = await this.$axios.post('/message', params); this.$router.push('/result'); } catch(e) { const message = e || 'Sorry, an error occurred.' window.alert(message); } } } } </script> -
結果を表示するページ
<template> <main> <span>Thank you!</span> </main> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { } } } </script> -
Netlify FunctionsのLambda関数
'use strict'; const fetch = require('node-fetch'); export const header = { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*', 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials': 'true', 'content-type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8', }; exports.handler = async (event, context, callback) => { if (event.httpMethod !== 'POST') { callback(null, { statusCode: 503, headers: header, body: JSON.stringify({error: 'Method Not Allowed'}) }); } try { const data = JSON.parse(event.body); const options = { method: 'post', body: { name: data.name, message: data.message}, headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'X-EXAMPLE-Authorization': 'XXXXX'} }; const resp = await fetch('https://exmaple.com/api/v1/message', options); callback(null, { statusCode: 200, headers: header, body: JSON.stringify(resp) }); } catch(err) { callback(null, { statusCode: 500, headers: header, body: JSON.stringify(err) }); } };